Implementation
The curriculum and teaching of international education aims at cultivating global citizens with four aspects and its development is inseparably interconnected to international exchanges and school internationalization. For integrating international education into various subject areas, schools can implement international education courses through issue integration, international project-based learning exchanges, or combing international exchanges, etc., and focus on concept-based learning, inquiry and practice, and multiple assessment.
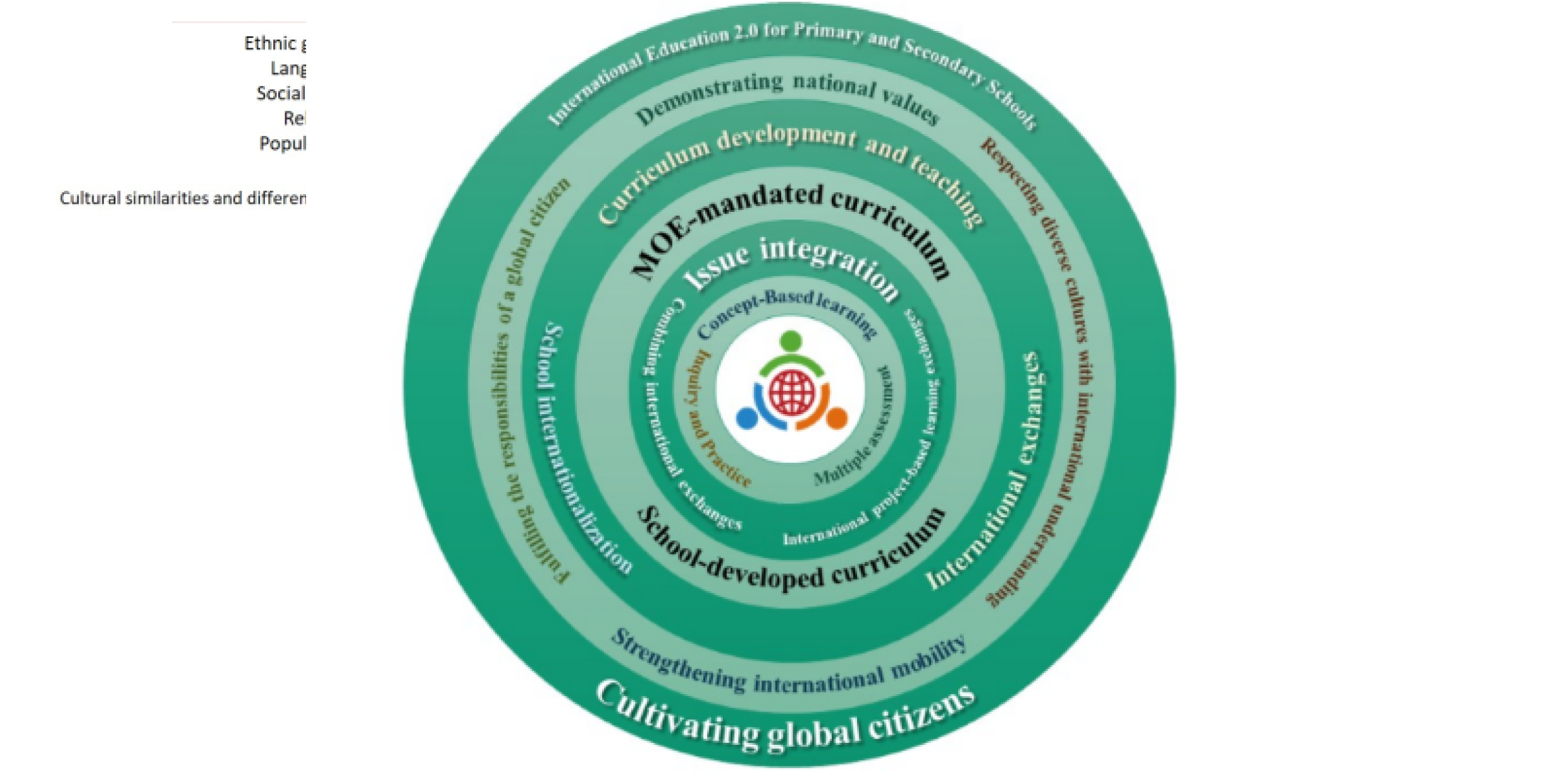
Issue Integration:
Formal courses with related activities such as informal courses.
International Project-Based Learning Exchanges:
Participating in various international project-based learning platforms (such as IEARN, Schools Online, etc.).
Combining International Exchanges:
Developing international education curriculum with international partner schools and presenting curriculum outcomes during international exchanges.
MOE-mandated curriculum:
Integrating international education topics into the formal curriculum, including a single subject or interdisciplinary courses. For every learning stages.
Alternative curriculum:
Using alternative learning courses, and international education topics as the center of the curriculum to integrate learning in related areas. For elementary and junior high schools.
School developed required courses and Elective courses in High school:
Develop international education school-based featured courses based on school vision and characteristics, including school developed required courses and elective courses. Strengthening students' global competence on knowledge and skill integration as well as daily life application by using thematic and topical inquiry, practical/experimental courses or exploratory experiences.
Concept-based Curriculum Design:
The international education curriculum is competency-oriented with the aim of cultivating students' abilities of interdisciplinary thinking and action taking in the learning process. The curriculum design needs to guide students to apply important concepts and skills to distinguish patterns and connections, and equip them with transferable understandings. Therefore, in the concept-based curriculum design, developing the guiding questions is an important step in designing teaching units. By identifying key concepts and keeping "what must students understand at the conceptual level?" in mind, it helps the curriculum design move from factual understanding to synergistic conceptual thinking.
Planning Inquiry and Action Tasks:
In response to a competency-based curriculum design, the development of teaching activities should be able to guide the main inquiry and action tasks, from which the tasks integrate the important learning points of the curriculum. Students can also demonstrate the competencies cultivated by the curriculum through the completion of these tasks.
Multiple Assessment Methods:
The assessment design should be able to concretely and authentically capture students' multi-dimensional competency performances. Multiple assessment methods should be used, and they should be implemented at appropriate times in conjunction with curriculum teaching activities, in order to reflect students' competency performance in the curriculum. Therefore, in addition to using multiple methods, whether teachers can appropriately plan formative and summative assessments and balance different types of assessment results is also a key focus of implementing multiple assessments.